Invasion History
First Galapagos Record: 1989General Invasion History:
Lyrodus pedicellatus was described from Spain but is probably of Indo-Pacific origin. It is now widespread in tropical-to-warm-temperate waters around the globe and its precise native range cannot be determined yet. It was described from the Bay of Biscay, Spain, in 1849 and has been collected and redescribed under many synonymous names (Turner 1966; Turner 1971). One description, as ‘Teredo chlorotica’ was made in Boston Harbor, Massachusetts, from the hull of a whaling ship which had cruised in the Pacific Ocean (Gould 1870). It was first collected on the Pacific coast of the US in the 1870s and appears to be localized in shallow harbors where water temperatures are warm enough for breeding (Carlton 1979). This species and an unidentified Lyrodus sp. were said to have established temporary populations in thermal effluents in England and Barnegat Bay, New Jersey (Coughlan 1977; Hoagland and Turner 1980). It may be that 'Lyrodus pedicellatus' represents a complex of numerous species, but further work needs to be conducted (Borges et al. 2012; Borges et al. 2014b). This shipworm has a short (up to 36 hours) larval duration in the plankton, so long-distance dispersal is largely by ships or driftwood (Lebour 1946).
Invasion History in the Galapagos:
Lyrodus pedicellatus was collected at Puerto Manta, Isla Baltra, Galapagos Islands. It was second in abundance on wooden panels, and most abundant on mangrove wood (1989, Cruz 1996).
Invasion history elsewhere in the world:
Lyrodus pedicellatus is now widespread in warm-temperate to tropical waters around the world, including the Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean and Black Seas, Indian Ocean, and West Pacific (Wallour 1960; Turner 1966; Srinivasan 1968; Sen et al. 2010; Museum of Comparative Zoology 2012). We regard it as cryptogenic over most of this range. It is apparently introduced in False Bay, South Africa (in 1931, Mead et al. 2011b), New Zealand (McKoy 1980; Cranfield et al. 1998), and the Galapagos Islands (Cruz 1996; Carlton et al. 2019). In the Tagus estuary, Portugal it replaced and apparently eliminated Teredo navalis from the 1960s–70s to the 1990s–2000s (Borges et al. 2010). In England, specimens are known from ships’ hulls and from thermal discharges (Turner 1966; Coughlan 1977). However, this species is now established and dominant in the English Channel, apparently as a result of increased temperatures (Borges 2007, cited in Borges et al. 2010).
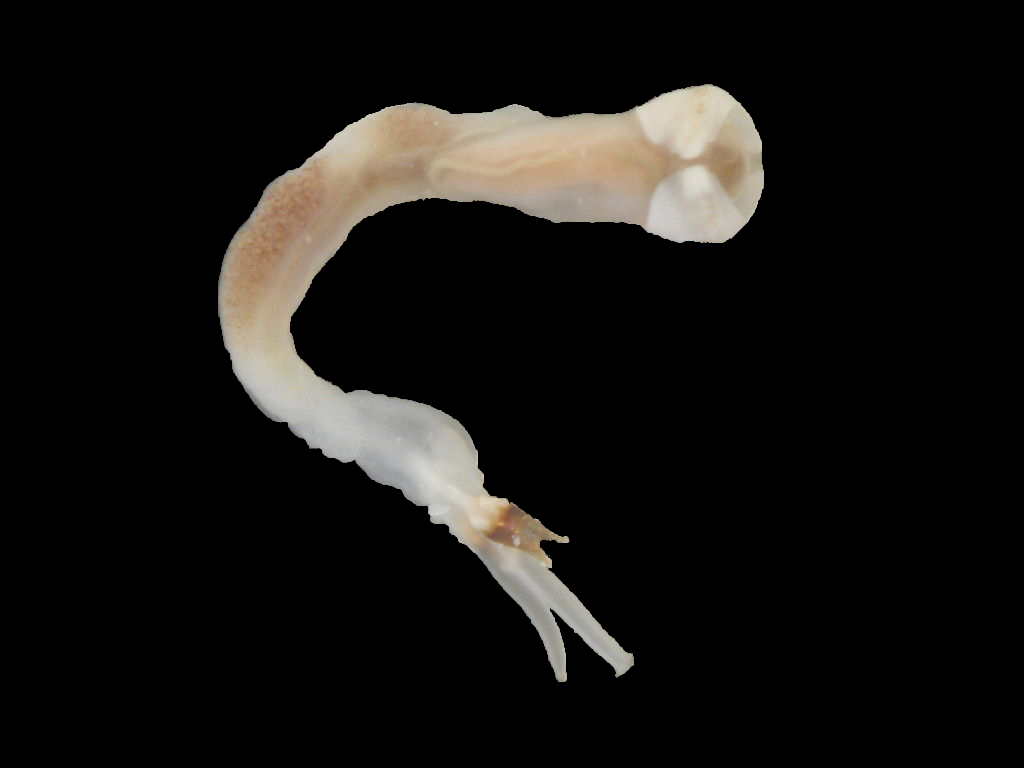
Description
Lyrodus pedicellatus is commonly known as the Blacktip Shipworm. It belongs to the family Teredinidae (shipworms), which are highly modified mollusks, hardly recognizable as bivalves, adapted for boring into wood. The shell is reduced to two small, ridged valves, covering the head, and is used for grinding and tearing wood fibers. The body is naked and elongated, and ends with two siphons, protected by elaborate calcareous structures called pallets (Turner 1966).
In the genus Lyrodus, the shell resembles that of the Naval Shipworm (Teredo navalis), but is smaller and more finely sculptured. The pallets have a calcareous base, which is conical distally and a brown to black cap made of periostracum. The outline resembles that of the stem and cup of a wineglass. The cap has straight sides, while the outer margin varies from a shallow U-shape to being deeply excavated, so that the conical, calcareous base protrudes (Turner 1966; Turner 1971; Coan et al. 2000). In one study, off Mumbai, India, the largest specimens reached 205 mm (Raveendram and Wagh 1991).
Genetic analysis of Lyrodus pedicellatus in the northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea indicates that these two populations may represent two cryptic species (Borges et al. 2012). Further genetic analysis is needed to evaluate the possibility of cryptic species and cryptic invasions throughout the reported range of L. pedicellatus.
Potentially misidentified species - The diversity of shipworms in tropical waters is very great. Many are now widely distributed in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, largely as a result of shipping. The species listed have been reported in Florida, the Caribbean, the West Coast of North America, or Hawaiian waters.
Taxonomy
Taxonomic Tree
| Kingdom: | Animalia | |
| Phylum: | Mollusca | |
| Class: | Bivalvia | |
| Subclass: | Heterodonta | |
| Order: | Myoida | |
| Superfamily: | Pholadoidea | |
| Family: | Teredinidae | |
| Genus: | Lyrodus | |
| Species: | pedicellatus |
Synonyms
Teredo chlorotica (Gould, 1870)
Teredo pertingens (Iredale, 1932)
Teredo (Lyrodus) hibicola (Koronuma, 1931)
Teredo (Pingoteredo) tristi (Iredale, 1936)
Teredo (Teredo) honoluluensis (Edmondson, 1946)
Teredo (Teredo) india (Nair, 1956)
Teredo (Teredo) madrasensis (Nair, 1956)
Teredo (Teredops) diegensis midwayensis (Edmondson, 1946)
Teredo (Teredops) hawaiensis (Dall, Bartsch, and Rehder, 1938)
Teredo (Teredops) kauiensis (Dall, Bartsch, and Rehder, 1938)
Teredo (Teredops) tateyamensis (Koronuma, 1931)
Teredo calmani (Roch, 1931)
Teredo dagmarae (Roch, 1931)
Teredo dalli (Moll and Roch, 1931)
Teredo franziusi (Roch, 1929)
Teredo helleniusi (Moll, 1936)
Teredo kiiensis (Taki and Habe, 1945)
Teredo lomensis (Roch, 1929)
Teredo malaccana (Roch, 1935)
Teredo nodosa (Roch, 1929)
Teredo pedicellata (de Quatrefages, 1849)
Teredo pedicellata truncata (Jeffreys, 1865)
Teredo pochhammeri (Moll, 1931)
Teredo robsoni (Roch, 1931)
Teredo samoanensis (Bartsch, 1927)
Teredo siamensis (Bartsch, 1927)
Teredo togoensis (Roch, 1929)
Teredo townsendi (Bartsch, 1922)
Teredo yatsui (Moll, 1929)
Teredo hawaiensis (Dall, Bartsch & Rehder, 1938)
Potentially Misidentified Species
Cosmopolitan, tropical, subtropical
Lyrodus floridanus
W Atlantic, subtropical. It was synonymized with L. pedicellatus, but later found to differ in its life history and geneitcs (Borges et al. 2012).
Lyrodus medilobatus
Cosmopolitan, tropical, subtropical
Lyrodus takanoshimensis
Cosmopolitan, tropical, subtropical, temperate, introduced in NE Pacific (British Columbia)
Nototeredo knoxi
Subtropical W Atlantic, oceanic
Psiloteredo megotara
N Atlantic, oceanic
Teredo bartschi
Cosmopolitan, tropical, subtropical, introduced in NE Pacific
Teredo clappi
Cosmopolitan, tropical, subtropical
Teredo fulleri
Cosmopolitan, tropical,
Teredo furcifera
Cosmopolitan, tropical, subtropical
Teredo navalis
Cryptogenic in NE Atlantic, NW Pacific, and Indo-West Pacific, but introduced in NW Atlantic, S Atlantic, NE Pacific, and SW Pacific
Teredora malleolus
Temperate-subtropical Atlantic, oceanic
Ecology
General:
Shipworms dig long burrows in submerged wood in marine environments. They burrow by rocking and abrading the wood fibers. The mantle covers most of the length of the body, and secretes a calcareous lining along the interior of the burrow. They normally have their anterior end, with head and shells inside the burrow, and their siphons protruding. The pallets plug the burrow when the siphons are retracted (Barnes 1983).
Shipworms are protandrous hermaphrodites, beginning life as male and transforming to female, but they have no capacity for self-fertilization. Males release sperm into the water column, which fertilizes eggs for the female. The fertilized eggs are then brooded in the gills. Larvae are retained in the gills to the veliger stage. Lyrodus pedicellatus, releases its larvae in an advanced stage, as pediveligers, which spend only 2 to 24 hours in the plankton (Turner and Johnson 1971). The larvae settle in the pediveliger stage, and then rapidly metamorphose and begin boring into wood within 2–3 days. They quickly develop a calcified shell, pallets, and burrow lining (Turner and Johnson 1971). Shipworms may obtain some (or most, Paalvast and van der Velde 2013) of their nutrition from plankton, but some comes from wood, which consists largely of cellulose. Symbiotic bacteria fix nitrogen, essential for protein synthesis (Turner and Johnson 1971; Barnes 1983).
Lyrodus pedicellatus is known from fixed wood structures and panels, and from driftwood in tropical and subtropical climates. In New Zealand, it was absent in mangrove habitats (Turner 1966; McKoy 1980), but it is reported to be abundant, together with five other shipworm species, in mangrove forests of southeastern India (Nair 1984). In experiments, L. pedicelllatus from California and New Guinea did not tolerate salinities below 20–25 PSU (Eckelbarger and Reish 1972; Rayner 1979). However, this shipworm is present in the Black Sea (~18–20 PSU) (Sen et al. 2010). This shipworm survived winter temperatures as low as 4.7 °C in England (Borges 2007, cited by Borges et al. 2011).
Food:
Phytoplankton, detritus
Trophic Status:
Suspension Feeder
SusFedHabitats
| General Habitat | Coarse Woody Debris | None |
| General Habitat | Marinas & Docks | None |
| General Habitat | Vessel Hull | None |
| Salinity Range | Polyhaline | 18-30 PSU |
| Salinity Range | Euhaline | 30-40 PSU |
| Tidal Range | Mid Intertidal | None |
| Tidal Range | Subtidal | None |
| Tidal Range | Low Intertidal | None |
| Vertical Habitat | Epibenthic | None |
Life History
Tolerances and Life History Parameters
| Minimum Temperature (ºC) | 11 | Experimental 50% survival, 7 days (Ecklebarger and Reish 1972). |
| Minimum Salinity (‰) | 21.6 | Experimental, 50% survival, 7 days (Ecklebarger and Reish 1972). |
| Minimum Reproductive Temperature | 14 | Carlton 1979 |
| Maximum Reproductive Temperature | 24 | Experimental, highest tested (Ecklebarger and Reish 1972). |
| Minimum Reproductive Salinity | 21.6 | Experimental, 50% survival, 7 days (Ecklebarger and Reish 1972). |
| Minimum Duration | 0.2 | Larval duration (Turner and Johnson 1971) |
| Maximum Duration | 1 | Larval duration (Turner and Johnson 1971) |
| Maximum Length (mm) | 205 | off Mumbai, India (Raveendram and Wagh 1991) |
| Broad Temperature Range | None | Warm temperate-Tropical |
| Broad Salinity Range | None | Polyhaline-Euhaline |
General Impacts
Specific impacts of Lyrodus pedicellatus are difficult to determine, because this shipworm often co-occurs with Teredo navalis (Naval Shipworm) and a few other species (Psiloteredo megotara, North Atlantic; Bankia gouldi, Northwest Atlantic; Bankia setacea, Northeast Pacific) in temperate waters, and with a more diverse community of shipworms in subtropical and tropical waters. However, L. pedicellatus was the dominant, or one of the most abundant, shipworm species in many tropical, subtropical, and warm-temperate harbors and bays (Wallour 1960; Turner 1966; Ibrahim 1981; Nair 1984; Raveendran and Wagh 1991).
Lyrodus pedicellatus is a common shipworm in the warmer waters of the world. Its economic impacts include the devouring of historic and modern wooden boats, ships, wharves, pilings, and other structures (Atwood 1922; Turner 1971; Turner and Johnson 1971; Wallour 1960). They can affect structures used in fisheries and aquaculture (Nair 1984), and affect the timber industry in regions where logs are stored in seawater before processing (Tsunoda 1979).
Ecological effects of the L. pedicellatus invasion include competition with other shipworm species (Borges et al. 2011); wood breakdown and the incorporation of wood into marine food webs (Barnes 1983); and providing habitat by riddling wood with tunnels and galleries used by many small mobile animals (polychaetes, amphipods, isopods, etc.) (Carlton 1979). Measures to control the impacts of shipworms on vessels and marine infrastructure include the use of metal, plastic, or toxic substances (creosote, copper salts, etc.) to avoid shipworm attacks (Atwood 1922; Sen et al. 2010), with adverse effects on other marine organisms and possible toxicity to animal and human consumers.
Regional Distribution Map
| Bioregion | Region Name | Year | Invasion Status | Population Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEP-Z | 1989 | Def | Estab |
Occurrence Map
| OCC_ID | Author | Year | Date | Locality | Status | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|
References
Abbott, R. Tucker (1974) American Seashells, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York. Pp. <missing location>Atwood, W. G. (1922) Marine borers, Proceedings of the American Society of Civil Engineers 48(6): 1408-1424
Barnard, J. Laurens; Reish, Donald J. (1959) Ecology of Amphipoda and Polychaeta of Newport Bay, California, Allen Hancock Foundation Occasional Publications 21: 1-106
Barnes, Robert D. (1983) Invertebrate Zoology, Saunders, Philadelphia. Pp. 883
Bartsch, Paul (1922) A monograph of the American shipworms, United States National Museum Bulletin 122: 1-48
Bastida R.; Torti M. R. (1972) [Boring organisms of the Argentine coasts. The presence of Lyrodus pedicellatus (Quatrefages 1849) (Mollusca, Pelecypoda) in the port of Mar del Plata, Key to South American Teredinae., Physis 31(82): 31-50
Borges, L. M. S. (2013) Biodegradation of wood exposed in the marine environment: Evaluation of the hazard posed by marine wood-borers in fifteen European sites, International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 96: 97-104
Borges, L. M. S.; Sivrikaya, H.; Le Roux, A.; Shipway, J. R.; Cragg, S. M.; Costa, F. O. (2012) Investigating the taxonomy and systematics of marine wood borers (Bivalvia : Teredinidae) combining evidence from morphology, DNA barcodes and nuclear locus sequences, Invertebrate Systematics 26: 572-582
Borges, L. M. S.; Valente, A. A.; Palma, P.; Nunes, L. (2010) Changes in the wood boring community in the Tagus Estuary: a case study, Marine Biodiversity Records 3: e41
Borges, Luisa M. S.; Costa, Filipe O. (2014) New records of wood-borers (Bivalvia: Teredinidae) and Isopoda, Limnoriidae) from Sao Miguel, Azores with a discussion of some aspects of their biogeography, Acoreana Supplement 10: 109-116
Borges, Luísa M. S.; Merckelbach, Lucas M.; Sampaio, Íris; Cragg, Simon M. (2014b) Diversity, environmental requirements, and biogeography of bivalve wood borers (Teredinidae) in European coastal waters, Frontiers in Zoology 11(13): Published online
Campos, Bernardita; Ramorino, Luis (1990) [Larvae and postlarvae of the Pholadacea of Chile], Revista de Biologia Marina 25: 15-63
Carlton, James T. (1979) History, biogeography, and ecology of the introduced marine and estuarine invertebrates of the Pacific Coast of North America., Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Davis. Pp. 1-904
Carlton, James T.; Eldredge, Lucius (2009) Marine bioinvasions of Hawaii: The introduced and cryptogenic marine and estuarine animals and plants of the Hawaiian archipelago., Bishop Museum Bulletin in Cultural and Environmental Studies 4: 1-202
Coan, Eugene V.; Valentich-Scott, Paul; Bernard, Frank R. (2000) Bivalve Seashells of Western North Ameira, Santa Barbara Museum of Natural history, Santa Barbara CA. Pp. <missing location>
Cohen, Andrew N.; Carlton, James T. (1995) Nonindigenous aquatic species in a United States estuary: a case study of the biological invasions of the San Francisco Bay and Delta, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and National Sea Grant College Program (Connecticut Sea Grant), Washington DC, Silver Spring MD.. Pp. <missing location>
Coles S. L., DeFelice R. C., Eldredge, L. G. (2002b) Nonindigenous marine species at Waikîkî and Hawai`i kai, Oahu, Hawai`i, Bishop Museum Technical Report 25: 1-255
Coles, S. L.; DeFelice, R. C. : Eldredge, L. G. (2002a) Nonindigenous marine species in Kaneohe Bay, Oahu, Hawai`i, Bishop Museum Technical Report 24: 1-364
Coles, S. L.; DeFelice, R. C.; Eldredge, L. G.; Carlton, J. T. (1999b) Historical and recent introductions of non-indigenous marine species into Pearl Harbor, Oahu, Hawaiian Islands., Marine Biology 135(1): 147-158
Coles, S. L.; Reath, P. R.; Skelton, P. A.; Bonito, V; DeFelice; Basch, L. (2003) Introduced marine species in Pago Pago Harbor, Fagatele Bay and the National Park Coast, American Samoa., Bishop Museum Technical Report 26: 1-24
Coughlan, J. (1977) Marine borers in Southampton Water, Proceedings of the Hampshire Field Club and Archaeological Society 33: 5-15
Cranfield, H.J.; Gordon, D.P.; Willan, R.C.; Marshall, B.A; Battershill, C.N.; Francis, M.P.; Nelson, W.A.; Glasby, C.J.; Read, G.B. (1998) <missing title>, The National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, New Zealand. Pp. <missing location>
Cruz, Manuel; Torres, Glasys; Villamar, Felicia (1989) Comparative study of the woodboring bivalves of the more resistant woods (Laurel, 'Moral', Cow Tree) and the more vulnerable (Mangrove) on the coast of Ecuador], Acta Oceanografica del Pacifico 5(1): 49-55
Dall, William Healey (1889) A preliminary catalogue of the shell-bearing marine mollusks and brachiopods of the south-eastern coast of the United States, Bulletin of the United States National Museum 37: 1-221
Eckelbarger, Kevin J.; Reish, Donald J. (1972) Effects of varying temperatures and salinities on settlement, growth, and reproduction of the wood-boring pelecypod, Lyrodus pedicellatus, Bulletin of the Southern California Academy of Sciences 71: 116-127
Farrapeira, Cristiane Maria Rocha; Tenório, Deusinete de Oliveira ; do Amaral, Fernanda Duar (2011) Vessel biofouling as an inadvertent vector of benthic invertebrates occurring in Brazil, Marine Pollution Bulletin 62: 832-839
Gould, Augustus A. (1870) <missing title>, Wright and Potter, State Printers, Boston. Pp. <missing location>
Harvard Museum of Comparative Zoology 2008-2021 Museum of Comparative Zoology Collections database- Malacology Collection. <missing URL>
Hoagland, K. E.; Turner, R. D. (1980) Range extensions of teredinids (shipworms) and polychaetes in the vicinity of a temperate-zone nuclear generating station., Marine Biology 58(1): 55-64
Ibrahim, J. V. (1981) Season of settlement of a number of shipworms (Mollusca: Bivalvia) in six Australian harbors., Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 32: 591-604
Lebour, Marie V. (1946) The species of Teredo in Plymouth waters, Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 26: 381-389
Lomonaco, Cecilia; Santos, Andre S.; Christoffersen, Martin l. (2011) Effects of local hydrodynamic regime on the individual’s size in intertidal Sabellaria (Annelida: Polychaeta: Sabellariidae) and associated fauna at Cabo Branco beach, north-east Brazil, Marine Biodiversity Records 4(e76): Published online
doi:10.1017/S1755267211000807;
McKoy, J. L (1980) Distribution of shipworms (Bivalvia: Teredinidae) in the New Zealand region, New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 14(3): 263-275
Mead, A.; Carlton, J. T.; Griffiths, C. L. Rius, M. (2011b) Introduced and cryptogenic marine and estuarine species of South Africa, Journal of Natural History 39-40: 2463-2524
Nair, N. Balakrishnan (1984) The problem of marine timber destroying organisms along the Indian coast, Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences 93(3): 203-223
Nepal, Vaskar; Fabrizio, Mary C. (2020) Sublethal effects of salinity and temperature on non-native blue catfish: Implications for establishment in Atlantic slope drainages, PLOS ONE 15(12): e0244392
Paalvast, Peter; van der Velde, Gerard (2013) What is the main food source of the shipworm Teredo navalis? A stable isotope approach, Journal of Sea Research 80: 58-60
Pati, M. V.; Rao, M. V.; Balaji, M.; Swain, D. (2012) Growth of wood borers in a polluted Indian harbour, World Journal of Zoology 7: 210-215
Rai Singh, Harinder Sasekumar, A. (1994) Distribution and abundance of marine wood borers on the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia., Hydrobiologia 285: 111-121
Rai Singh, Harinder; Sasekumar, A. (1996) Wooden panel deterioration by tropical marine wood borers, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 42: 755-769
Raveendran, T. V.; Wagh, A. B. (1991) Distribution and growth of wood-borers in Bombay offshore waters., Indian Journal of Marine Science 20: 143-146
Rayner, Suzanne M (1979) Comparison of the salinity range tolerated by Teredinids (Mollusca: Teredinidae) under controlled conditions with that observed in an estuary in Papua New Guinea., Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 30: 521-533
Ruiz, Gregory M.; Geller, Jonathan (2018) Spatial and temporal analysis of marine invasions in California, Part II: Humboldt Bay, Marina del Re, Port Hueneme, and San Francisco Bay, Smithsonian Environmental Research Center & Moss Landing Laboratories, Edgewater MD, Moss Landing CA. Pp. <missing location>
Scheltema, R. S. (1971) Dispersal of phytoplanktotrophic shipworm larvae (Bivalvia : Teredinidae) over long distances by ocean currents*, Marine Biology 11: 5--11
Sen, Selim; Sivrikaya, Huseyin; Yalcin, Mesut; Bakir, Ahmet Kerem; Öztürk, Bilal (2010) Fouling and boring organisms deteriorating various European and tropical woods on the Turkish coast line, African Journal of Biotechnology 9(17): 2566-2573
Sirmah, P. K.; Mburu, F. G.; Muisu, F. N.; Wahungu, G. M.; Waweru, C. W. (2009) Incidence and severity of marine borer attack at different depths at Mtongwe Jetty Pontoon, Mombasa, Kenya, African Journal of Ecology 47: 693-698
Srinivasan, V. V. (1968) Notes on the distribution of wood-boring teredines in the tropical Indo-Pacific, Pacific Science 12: 277-280
Tsunoda, Kunio (1979) Ecological studies of shipworm attack on wood in the sea water log storage site, Wood Research: Bulletin of the Wood Research Institute Kyoto University 65: 11-53
Turner, R. D.; Johnson, A. C. (1971) Marine Borers, Fungi, and Fouling Organisms of Wood, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris. Pp. 259-301
Turner, Ruth D. (1966) A survey and illustrated catalogue of the Teredinidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia), The Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University, Cambridge. Pp. <missing location>
Turner, Ruth D. (1971) Marine Borers, Fungi, and Fouling Organisms of Wood, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris. Pp. <missing location>
Wallour, Dorothy Brown (1960) Thirteenth progress report on marine borer activity in test boards operated during 1959, William F. Clapp Laboratories, Duxbury, Massachusetts. Pp. 1-41
Wasson, Kerstin; Zabin, C. J.; Bedinger, L.; Diaz, M. C.; Pearse J. S. (2001) Biological invasions of estuaries without international shipping: the importance of intraregional transport, Biological Conservation 102: 143-153